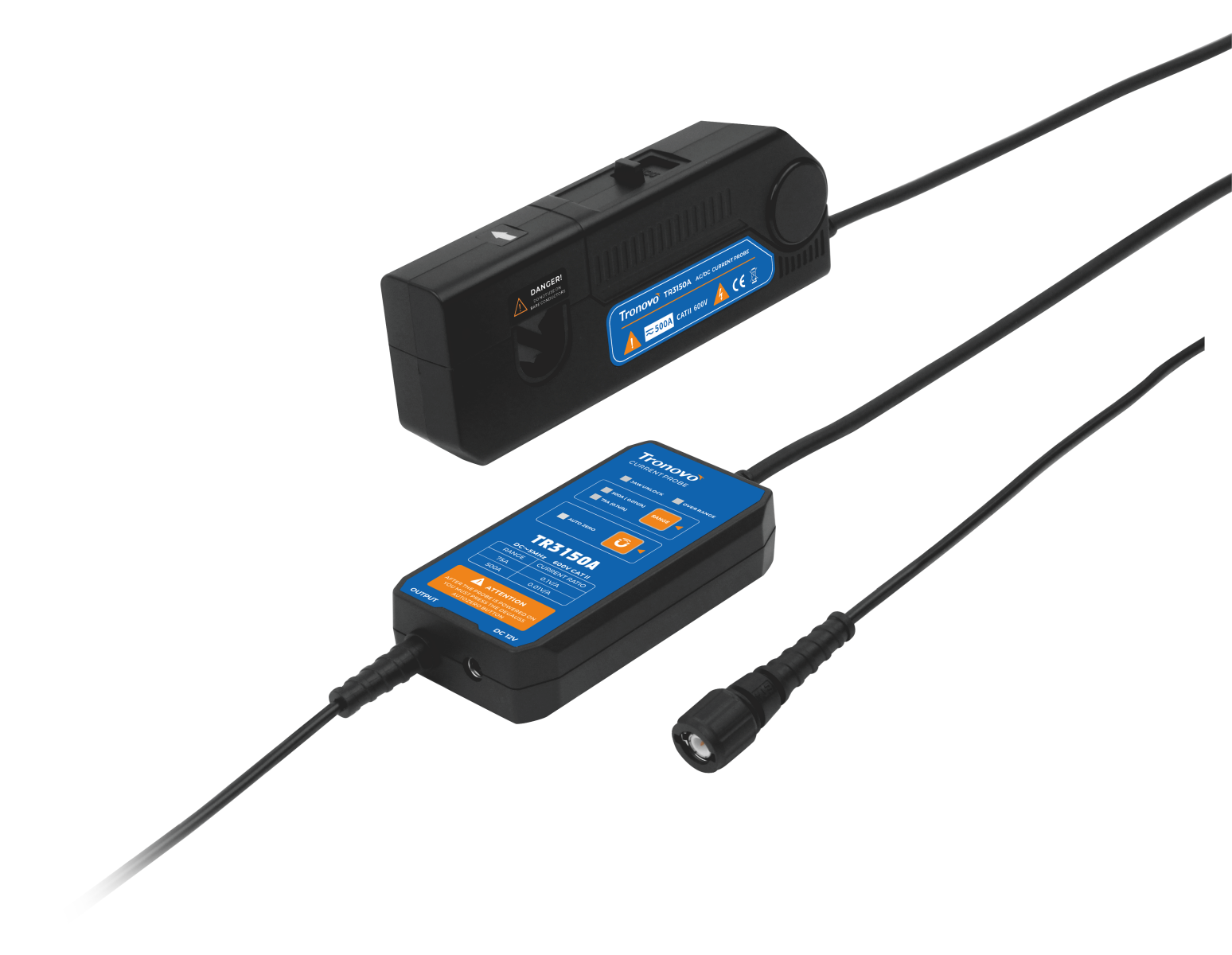
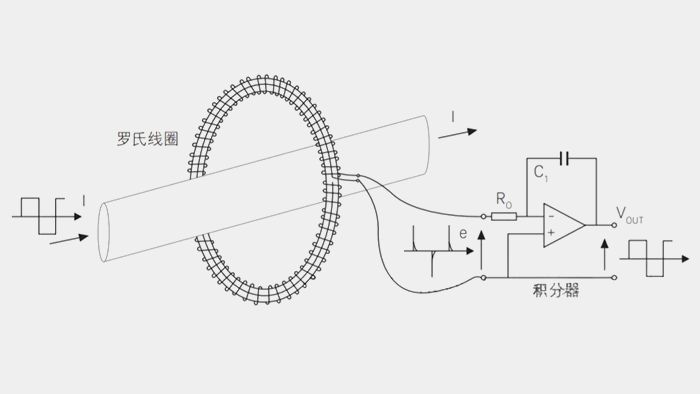
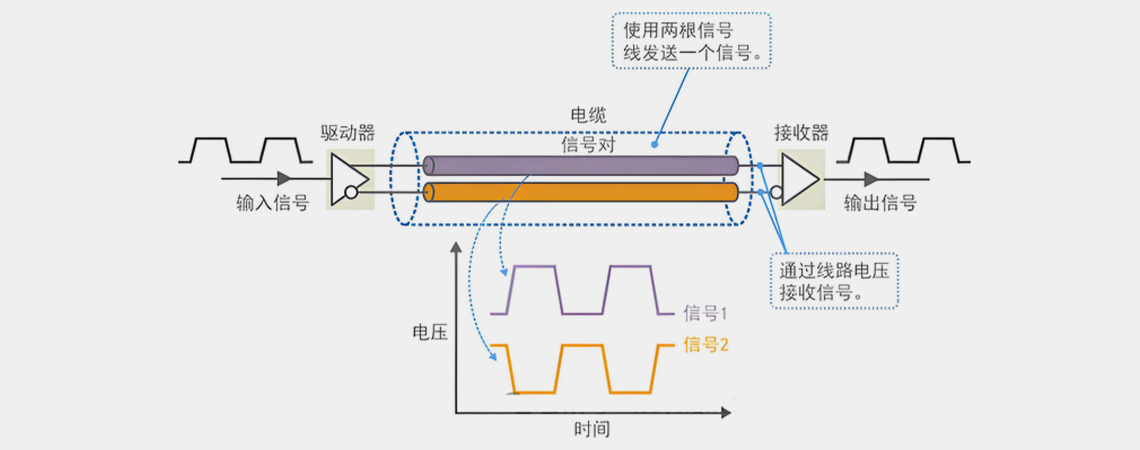
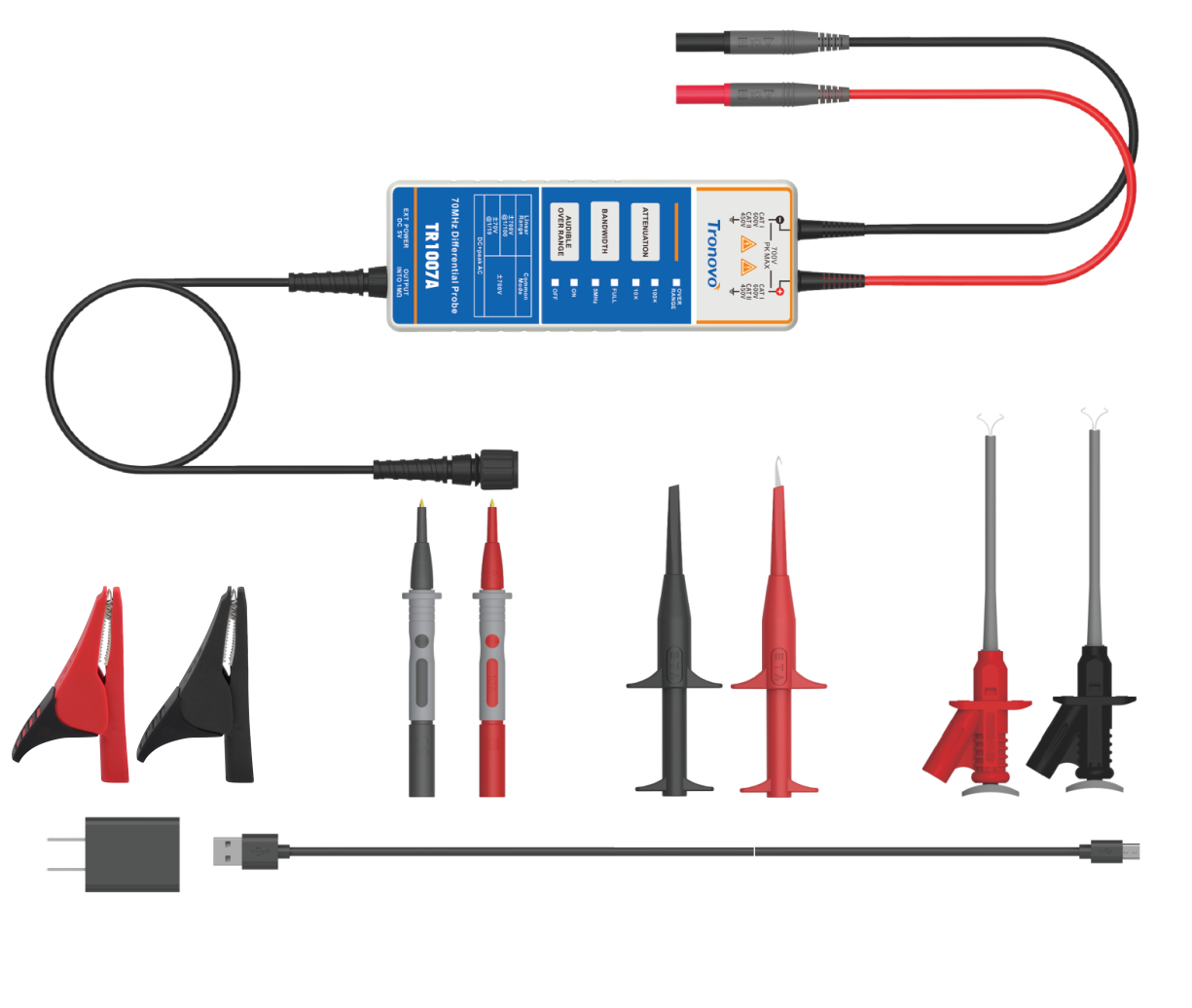
Differential probe (Differential Probe) and ordinary probe (Single-Ended Probe) are very different in design and use, one of which is their handling of parasitic capacitance.
A differential probe is designed to measure the voltage difference between two points, such as a differential signal or a differential pair. They typically have the following features, which help to reduce parasitic capacitance:
1. Differential input: The differential probe measures the voltage difference between the two inputs, not the voltage relative to ground. This design reduces the influence of the ground loop, thereby reducing the parasitic capacitance due to the ground line.
2. Shielding: Differential probes usually have better shielding design to reduce external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce parasitic capacitance between the probe and the circuit under test.
3. Low capacitive load: The differential probe is designed to have as little capacitive load as possible on the circuit under test, which means that the input capacitance of the probe is very low, thereby reducing the influence of parasitic capacitance.
4. High impedance: Differential probes usually have a high input impedance, which helps to reduce the capacitive effect when current flows through the probe.
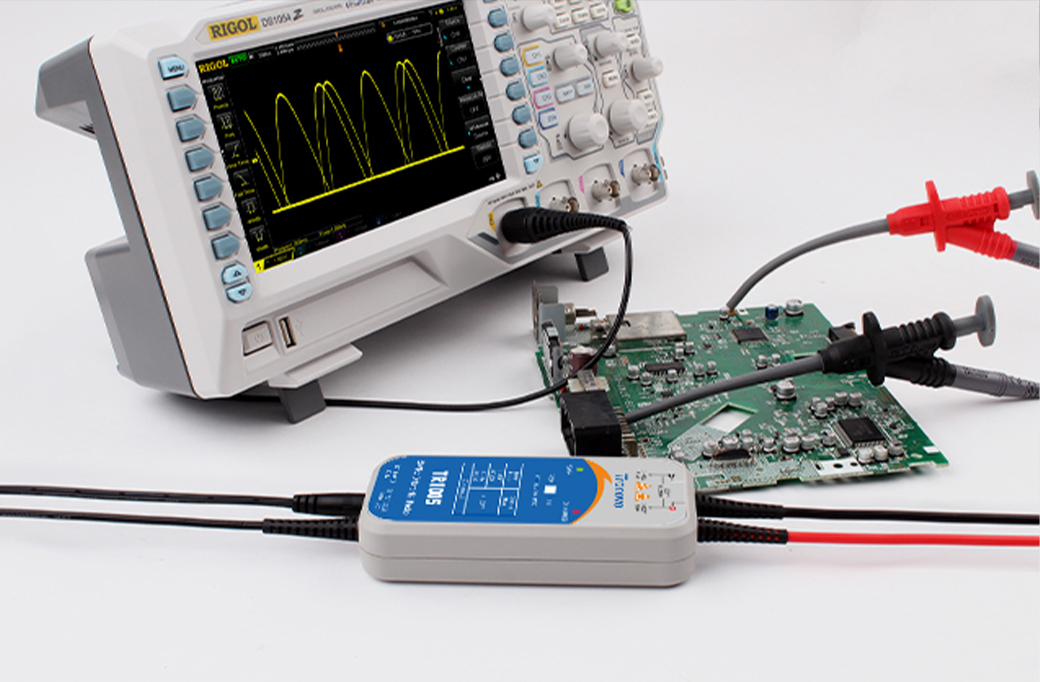
Ordinary probes (single-ended probes) usually measure voltage relative to ground, which may cause the following problems:
1. ground loop: single-ended probe needs to be connected to ground, which may introduce ground loop problems and increase parasitic capacitance.
2. Electromagnetic interference: Single-ended probes may be more susceptible to external electromagnetic interference, which may require more complex shielding to reduce parasitic capacitance.
3. Capacitive load: The single-ended probe may have a greater capacitive load on the circuit under test, which will increase the influence of parasitic capacitance.
In general, differential probes, through the particularity of their design and use, can more effectively reduce parasitic capacitance, thereby providing more accurate measurement results, especially in high-frequency and sensitive differential signal measurements.